Android So动态加载 优雅实现与原理分析
背景:漫品Android客户端集成适配转换功能(基于目标识别(So库35M)和人脸识别库(5M)),导致apk体积50M左右,为优化客户端体验,决定实现So文件动态加载.
开源地址: https://github.com/AnyMarvel/ManPinAPP
本文默认认为大家对JNI开发有一定的了解。在 Android 开发中调用动态链接库文件*.so都是通过 jni 的加载方式,一般的开发方式往往是在 apk 或 jar 包中调用so文件时,都要将对应 so 文件打包进 apk 或 jar 包。
基于以上的常见的方式,我们一般使用java提供的so加载api
System.loadLibrary(String libName):参数为so库名称,位于 apk 压缩文件中的 libs 目录,最后复制到 apk 安装目录下;System.load(String pathName):参数为 so 库在磁盘中完整的路径,可以加载自定义外部 so 库文件;使用第三方库ReLinker,有so加载成功、失败的回调,安全加载不崩溃。(relinker也是对上面两种api的封装,但更推荐大家使用这种加载方式)
看到上述API其实大家可以看出来System.load(String pathName)这个api其实已经可以实现So的动态加载,那为什么我们还要搞一些所谓的黑科技呢?
如果项目native库很多,还支持各种平台,为了减少apk size,so库动态下发,按需加载是不错的选择。比如x86库服务器下发,动态加载,瘦身效果将非常可观。但是采取常规load方式,改动有点大,底层jar包,第三库不好改加载路径。
在应用启动的时,一次注入本地so路径path,待程序使用过程中so准备后安全加载。(原因后面分析,我们先看下实践)
- 一. 下载So文件到sdk卡
- 二. copy So文件到app缓存空间
- 三. 修改nativeLibraryDirectories(6.0以下)或nativeLibraryPathElements(6.0及以上)(关键:把自定义的native库path插入native数组最前面,即使安装包libs目录里面有同名的so,也优先加载指定路径的外部so。)
- 四. 正常加载so使用
有兴趣可以直接查看开源代码:https://github.com/AnyMarvel/ManPinAPP
核心类,修改nativeLibraryDirectories列表,加载需要的so文件映射
/**
* com.google.android.apps.photolab.storyboard.soloader.LoadLibraryUtil
* Description:动态加载so文件的核心,注入so路径到nativeLibraryDirectories数组第一个位置,会优先从这个位置查找so
* 更多姿势,请参考开源库动态更新so的黑科技,仅供学习交流
*
*/
public class LoadLibraryUtil {
private static final String TAG = LoadLibraryUtil.class.getSimpleName() + "-duqian";
private static File lastSoDir = null;
public static synchronized boolean installNativeLibraryPath(ClassLoader classLoader, File folder)
throws Throwable {
if (classLoader == null || folder == null || !folder.exists()) {
Log.e(TAG, "classLoader or folder is illegal " + folder);
return false;
}
final int sdkInt = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
final boolean aboveM = (sdkInt == 25 && getPreviousSdkInt() != 0) || sdkInt > 25;
if (aboveM) {
try {
V25.install(classLoader, folder);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
try {
V23.install(classLoader, folder);
} catch (Throwable throwable1) {
V14.install(classLoader, folder);
}
}
} else if (sdkInt >= 23) {
try {
V23.install(classLoader, folder);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
V14.install(classLoader, folder);
}
} else if (sdkInt >= 14) {
V14.install(classLoader, folder);
}
lastSoDir = folder;
return true;
}
private static final class V23 {
private static void install(ClassLoader classLoader, File folder) throws Throwable {
Field pathListField = ReflectUtil.findField(classLoader, "pathList");
Object dexPathList = pathListField.get(classLoader);
Field nativeLibraryDirectories = ReflectUtil.findField(dexPathList, "nativeLibraryDirectories");
List<File> libDirs = (List<File>) nativeLibraryDirectories.get(dexPathList);
//去重
if (libDirs == null) {
libDirs = new ArrayList<>(2);
}
final Iterator<File> libDirIt = libDirs.iterator();
while (libDirIt.hasNext()) {
final File libDir = libDirIt.next();
if (folder.equals(libDir) || folder.equals(lastSoDir)) {
libDirIt.remove();
Log.d(TAG, "dq libDirIt.remove() " + folder.getAbsolutePath());
break;
}
}
libDirs.add(0, folder);
Field systemNativeLibraryDirectories =
ReflectUtil.findField(dexPathList, "systemNativeLibraryDirectories");
List<File> systemLibDirs = (List<File>) systemNativeLibraryDirectories.get(dexPathList);
//判空
if (systemLibDirs == null) {
systemLibDirs = new ArrayList<>(2);
}
Log.d(TAG, "dq systemLibDirs,size=" + systemLibDirs.size());
Method makePathElements = ReflectUtil.findMethod(dexPathList, "makePathElements", List.class, File.class, List.class);
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<>();
libDirs.addAll(systemLibDirs);
Object[] elements = (Object[]) makePathElements.invoke(dexPathList, libDirs, null, suppressedExceptions);
Field nativeLibraryPathElements = ReflectUtil.findField(dexPathList, "nativeLibraryPathElements");
nativeLibraryPathElements.setAccessible(true);
nativeLibraryPathElements.set(dexPathList, elements);
}
}
/**
* 把自定义的native库path插入nativeLibraryDirectories最前面,即使安装包libs目录里面有同名的so,也优先加载指定路径的外部so
*/
private static final class V25 {
private static void install(ClassLoader classLoader, File folder) throws Throwable {
Field pathListField = ReflectUtil.findField(classLoader, "pathList");
Object dexPathList = pathListField.get(classLoader);
Field nativeLibraryDirectories = ReflectUtil.findField(dexPathList, "nativeLibraryDirectories");
List<File> libDirs = (List<File>) nativeLibraryDirectories.get(dexPathList);
//去重
if (libDirs == null) {
libDirs = new ArrayList<>(2);
}
final Iterator<File> libDirIt = libDirs.iterator();
while (libDirIt.hasNext()) {
final File libDir = libDirIt.next();
if (folder.equals(libDir) || folder.equals(lastSoDir)) {
libDirIt.remove();
Log.d(TAG, "dq libDirIt.remove()" + folder.getAbsolutePath());
break;
}
}
libDirs.add(0, folder);
//system/lib
Field systemNativeLibraryDirectories = ReflectUtil.findField(dexPathList, "systemNativeLibraryDirectories");
List<File> systemLibDirs = (List<File>) systemNativeLibraryDirectories.get(dexPathList);
//判空
if (systemLibDirs == null) {
systemLibDirs = new ArrayList<>(2);
}
Log.d(TAG, "dq systemLibDirs,size=" + systemLibDirs.size());
Method makePathElements = ReflectUtil.findMethod(dexPathList, "makePathElements", List.class);
libDirs.addAll(systemLibDirs);
Object[] elements = (Object[]) makePathElements.invoke(dexPathList, libDirs);
Field nativeLibraryPathElements = ReflectUtil.findField(dexPathList, "nativeLibraryPathElements");
nativeLibraryPathElements.setAccessible(true);
nativeLibraryPathElements.set(dexPathList, elements);
}
}
private static final class V14 {
private static void install(ClassLoader classLoader, File folder) throws Throwable {
Field pathListField = ReflectUtil.findField(classLoader, "pathList");
Object dexPathList = pathListField.get(classLoader);
ReflectUtil.expandFieldArray(dexPathList, "nativeLibraryDirectories", new File[]{folder});
}
}
/**
* fuck部分机型删了该成员属性,兼容
*
* @return 被厂家删了返回1,否则正常读取
*/
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.M)
private static int getPreviousSdkInt() {
try {
return Build.VERSION.PREVIEW_SDK_INT;
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
}
return 1;
}
}
上面说了把自定义的native库path插入nativeLibraryDirectories最前面,那为什么这么做会生效呢
- 首先了解以下So的加载流程
- So热修复技术介绍及如何动态加载So
这里先做下准备工作
- Android源码在线浏览:http://androidxref.com
- Android源码下载:https://source.android.com/setup/downloading
- Android 源码下载使用国内镜像:https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/AOSP/
So文件加载流程 不同的同学请戳这里 Android 的 so 文件加载机制
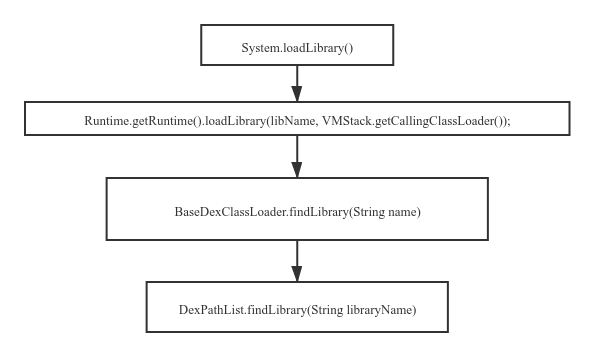
从System.loadlibrary() 方法分析so文件的加载流程,如下图所示:
System.loadLibrary()
//System.java
public static void loadLibrary(String libname) {
Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary0(VMStack.getCallingClassLoader(), libname);
}
此处VMStack.getCallingClassLoader()拿到的是调用者的ClassLoader,一般情况下是PathClassLoader。我们进入Runtime类的loadLibrary0()方法看看。
//Runtime.java
synchronized void loadLibrary0(ClassLoader loader, String libname) {
if (libname.indexOf((int)File.separatorChar) != -1) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Directory separator should not appear in library name: " + libname);
}
String libraryName = libname;
// 1. 如果classloder存在,通过loader.findLibrary()查找到so路径
if (loader != null) {
String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName);
if (filename == null) {
// It's not necessarily true that the ClassLoader used
// System.mapLibraryName, but the default setup does, and it's
// misleading to say we didn't find "libMyLibrary.so" when we
// actually searched for "liblibMyLibrary.so.so".
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(loader + " couldn't find \"" +
System.mapLibraryName(libraryName) + "\"");
}
String error = doLoad(filename, loader);
if (error != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
return;
}
// 2. 如果classloder不存在,通过loader.findLibrary()查找到so路径
String filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
List<String> candidates = new ArrayList<String>();
String lastError = null;
for (String directory : getLibPaths()) { // getLibPaths()代码在最下方
String candidate = directory + filename;
candidates.add(candidate);
if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(candidate)) {
String error = doLoad(candidate, loader);
if (error == null) {
return; // We successfully loaded the library. Job done.
}
lastError = error;
}
}
// 3. 都没找到,抛出 UnsatisfiedLinkError 异常
if (lastError != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(lastError);
}
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Library " + libraryName + " not found; tried " + candidates);
}
这里根据ClassLoader是否存在分了两种情况:
- 当ClasssLoader存在的时候通过loader的 findLibrary()查看目标库所在路径;
- 当ClassLoader不存在的时候通过getLibPaths()查找加载路径。 最终他们都会调用doLoad()加载动态库。
这里我们只查看ClasssLoader存在时的情况:
前面知道了这个ClassLoader其实是PathClassLoader,但是findLibrary位于PathClassLoader的父类BaseDexClassLoader中:
//BaseDexClassLoader.java
public String findLibrary(String name) {
return pathList.findLibrary(name);
}
其中pathList的类型为DexPathList,我们看看它的findLibrary()方法.关键点在DexPathList.findLibrary(String libraryName) 方法中
http://androidxref.com/5.0.0_r2/xref/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexPathList.java
/**
371 * Finds the named native code library on any of the library
372 * directories pointed at by this instance. This will find the
373 * one in the earliest listed directory, ignoring any that are not
374 * readable regular files.
375 *
376 * @return the complete path to the library or {@code null} if no
377 * library was found
378 */
379 public String findLibrary(String libraryName) {
380 String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
381 for (File directory : nativeLibraryDirectories) {
382 String path = new File(directory, fileName).getPath();
383 if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(path)) {
384 return path;
385 }
386 }
387 return null;
388 }
可以看到首先会调用System.mapLibraryName函数获得so的名字,比如我传入的参数是Test(这个Test就是在调用System.loadLibrary(“Test”)时传入的),则这个函数的作用就是将其转换为类似libTest.so这样的名字,然后遍历nativeLibraryDirectories数组,这是一个File文件夹数组,看其文件夹下是否存在对应的so,并且是否可读,如果满足条件,则直接返回。
那么我们就可以将我们的patch的so所在目录插入到这个数组最前面即可完成so的修复。具体代码就不贴了,实践后得出的结论是这种方式是完全可行的,只不过Android 6.0以后版本中这部分代码逻辑发生了改变。
在Android 4.0-5.1中,只需要将文件夹目录插入到nativeLibraryDirectories数组最前面即可,这个过程直接使用反射插入patch的so所在目录到数组最前面。(nativeLibraryDirectories存储了so文件加载的映射表,这里相当于修改了应用加载so的列表)
61 /** List of native library directories. */
62 private final File[] nativeLibraryDirectories;
但是在Android 6.0以后,查找逻辑转为了Elements查找
http://androidxref.com/9.0.0_r3/xref/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexPathList.java
/**
536 * Finds the named native code library on any of the library
537 * directories pointed at by this instance. This will find the
538 * one in the earliest listed directory, ignoring any that are not
539 * readable regular files.
540 *
541 * @return the complete path to the library or {@code null} if no
542 * library was found
543 */
544 public String findLibrary(String libraryName) {
545 String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
546
547 for (NativeLibraryElement element : nativeLibraryPathElements) {
548 String path = element.findNativeLibrary(fileName);
549
550 if (path != null) {
551 return path;
552 }
553 }
554
555 return null;
556 }
所以在6.0中需要将so的patch目录转换为Element对象,插入到nativeLibraryPathElements最前面,Element的对象可以直接用反射去实现下面的代码进行构造即可。
66 /** List of native library path elements. */
67 // Some applications rely on this field being an array or we'd use a final list here
68 /* package visible for testing */ NativeLibraryElement[] nativeLibraryPathElements;
最后的难点就是如何将对应cpu类型的so拿到,这个过程还是十分复杂的,比如说一个so同时存在x86,armeabi-v7a,armeabi的patch,而手机cpu是armeabi-v7a的,这时候就应该加载armeabi-v7a的so。总之这种情况组合起来会十分复杂了。但一般的厂商都是只兼容armeabi架构,其他的架构就可以向上兼容了(除x86架构外)
手机的cpu结构类型可以通过Build.CPU_ABI和Build.CPU_ABI2拿到,后面做的事就是根据这两个值去加载对应目录下的so,其实把这两个目录都插进去就没问题了。
总结:
到此处,那么so文件的动态加载(也可以叫做So文件的热修复)已经介绍完了,起始还是比较简单的,只是修改了so文件列表的数组映射,加载了需要使用的真实的so文件.
经过动态加载,漫品客户端也由原来50M的体积缩小到了15M的输出包.
安利 欢迎大家的start
开源地址: https://github.com/AnyMarvel/ManPinAPP
热修复so代码包位置: com.google.android.apps.photolab.storyboard.soloader.LoadLibraryUtil
如有问题请留言,或github issure